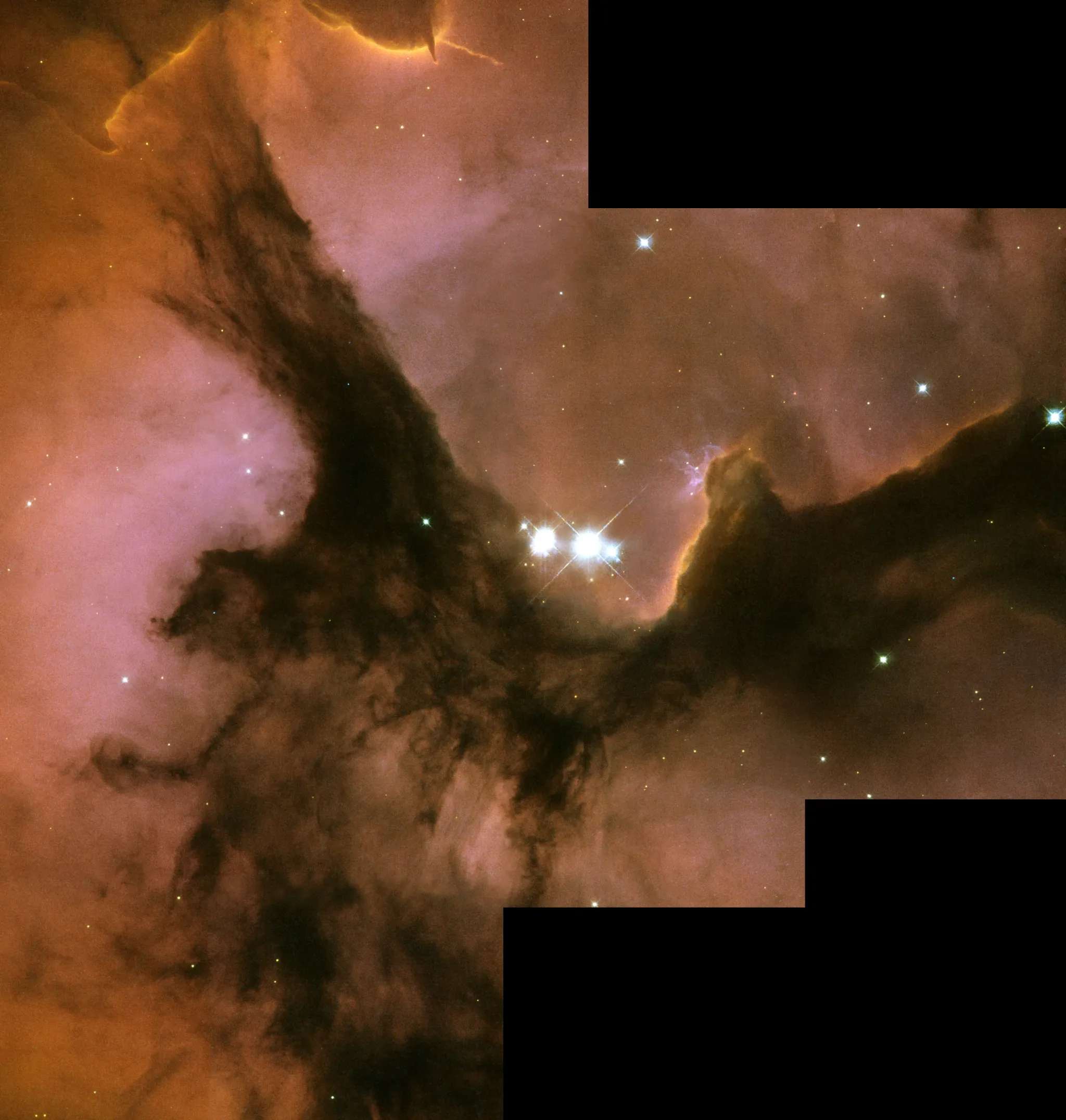
M20 | NGC 6514 | Trifid Nebula | Sagittarius | 5,200 Light Years Away
Our Best Image

Messier 20, also known as the Trifid Nebula, is a remarkable emission nebula located in the constellation Sagittarius. Discovered by Charles Messier in 1764, this celestial beauty is situated approximately 5,200 light-years away from Earth. The Trifid Nebula derives its name from the dark lanes of dust that divide it into three distinct parts, creating a stunning visual effect.
At the heart of Messier 20 lies a young open star cluster, designated NGC 6514, whose massive stars ionize the surrounding hydrogen gas, causing it to emit a vibrant reddish glow. The Trifid Nebula is a stellar nursery, actively forming new stars within its gas and dust clouds. Observations of Messier 20 across various wavelengths, from infrared to radio waves, provide astronomers with insights into the processes of star formation and the dynamic interactions between young stars and their cosmic environment.
One of the most captivating features of the Trifid Nebula is its combination of emission, reflection, and dark nebulae, creating a complex and visually striking scene. The dark lanes in the nebula are often referred to as “globules,” which are dense regions of dust and gas where new stars may be forming. The study of Messier 20 enhances our understanding of the lifecycle of stars and the intricate interplay of various astrophysical processes within the vast and dynamic tapestry of our Milky Way galaxy.